Let’s face it—renewable energy can feel like a jungle of confusing terminology. You’ve got solar energy, photovoltaic systems, solar thermal panels, and a dozen other terms thrown around. It’s like a renewable energy buffet, and you’re stuck wondering which dish to pick. One common question many people ask is: Is photovoltaic the same as solar? While the two terms are closely related, they’re not identical.
If you’re scratching your head over this, don’t worry—you’re not alone. Understanding the difference between solar energy and photovoltaic systems can be a game-changer for anyone planning to go green. Whether you’re a homeowner considering solar panels or just someone curious about sustainable energy, knowing the difference will help you make smarter decisions.
So, grab a cup of coffee (or tea if you’re feeling fancy), and let’s dive into this sunny topic!

Is Photovoltaic the Same as Solar? Understanding the Basics
No, photovoltaic is not the same as solar, but they’re deeply connected. To put it simply: solar is the big umbrella, and photovoltaic (PV) is just one part of it. Think of solar as the “parent” term that includes all energy derived from the sun. Photovoltaic, on the other hand, refers specifically to the technology that converts sunlight into electricity.
Let’s break it down:
- Solar Energy: A broad term that covers all ways of harnessing the sun’s power—whether it’s generating heat, producing electricity, or even growing plants (photosynthesis counts too, right?).
- Photovoltaic Technology: A specific type of solar technology that uses panels to convert sunlight directly into electricity through a scientific process called the photovoltaic effect.
In short, all photovoltaic systems are solar, but not all solar systems are photovoltaic. It’s like saying all apples are fruits, but not all fruits are apples.
This distinction is important because different types of solar technologies have different applications. For example, photovoltaic systems are ideal for generating electricity, while other solar systems, like solar thermal panels, are better for heating water or buildings.
Feeling brighter already? Let’s dig deeper into what solar energy is all about!
What is Solar Energy?
Solar energy is one of the most abundant and versatile sources of power available to us. It’s the energy we harness directly from the sun, and it’s been powering life on Earth for billions of years—plants, after all, have been using it for photosynthesis since the dawn of time. But in modern terms, solar energy refers to technology-driven ways of capturing the sun’s energy and converting it into something useful, like electricity or heat.
Here’s what makes solar energy such a hot (pun intended!) topic:
- Renewable and Sustainable: Unlike fossil fuels, solar energy is practically infinite. As long as the sun rises every day, we’ve got a steady supply of energy.
- Clean and Green: Solar doesn’t produce greenhouse gases or harmful emissions, making it an environmentally friendly alternative.
- Adaptable: Solar energy can be harnessed on a small scale (think rooftop panels) or a large scale (massive solar farms).
Types of Solar Energy Technologies
Solar energy isn’t a one-size-fits-all deal; it comes in several flavors, each with its own unique applications. Let’s break them down:
- Solar Photovoltaic (PV):
- This is the technology behind solar panels that convert sunlight directly into electricity.
- Photovoltaic systems are great for homes, businesses, and even portable devices like solar-powered chargers.
- Solar Thermal Energy:
- Instead of making electricity, this technology uses the sun’s heat to warm water, air, or other fluids.
- Common uses include solar water heaters and space heating systems.
- Concentrated Solar Power (CSP):
- A more industrial-level technology that uses mirrors to focus sunlight onto a small area, creating intense heat that drives turbines to generate electricity.
- Often used in large solar farms.
Why Is Solar Energy So Important?
Let’s look at some quick stats:
- In 2023, solar energy accounted for about 4% of global electricity generation, a number that’s rapidly climbing as the technology gets cheaper and more efficient.
- According to the International Energy Agency (IEA), solar power is expected to be the largest source of electricity by 2050.
- The cost of solar panels has dropped by more than 80% over the past decade, making it more accessible to everyday consumers.
But solar energy isn’t just about numbers—it’s about impact. With climate change becoming a pressing issue, the shift toward renewable energy sources like solar is critical for reducing our carbon footprint. And because it’s so versatile, solar energy can power everything from off-grid cabins to massive industrial operations.
Solar energy is a broad and flexible category that includes various technologies, each designed for a specific purpose. While photovoltaic systems are the stars of the show when it comes to generating electricity, other solar technologies play equally important roles in creating a sustainable energy future.
What Does Photovoltaic Mean?
The term photovoltaic might sound like something straight out of a science textbook, but it’s actually a lot simpler than it seems. The word itself breaks down into two parts:
- Photo = light
- Voltaic = electricity
Put them together, and you get the technology that converts sunlight directly into electricity—an incredible feat made possible by science!
Definition of Photovoltaic (PV) Systems
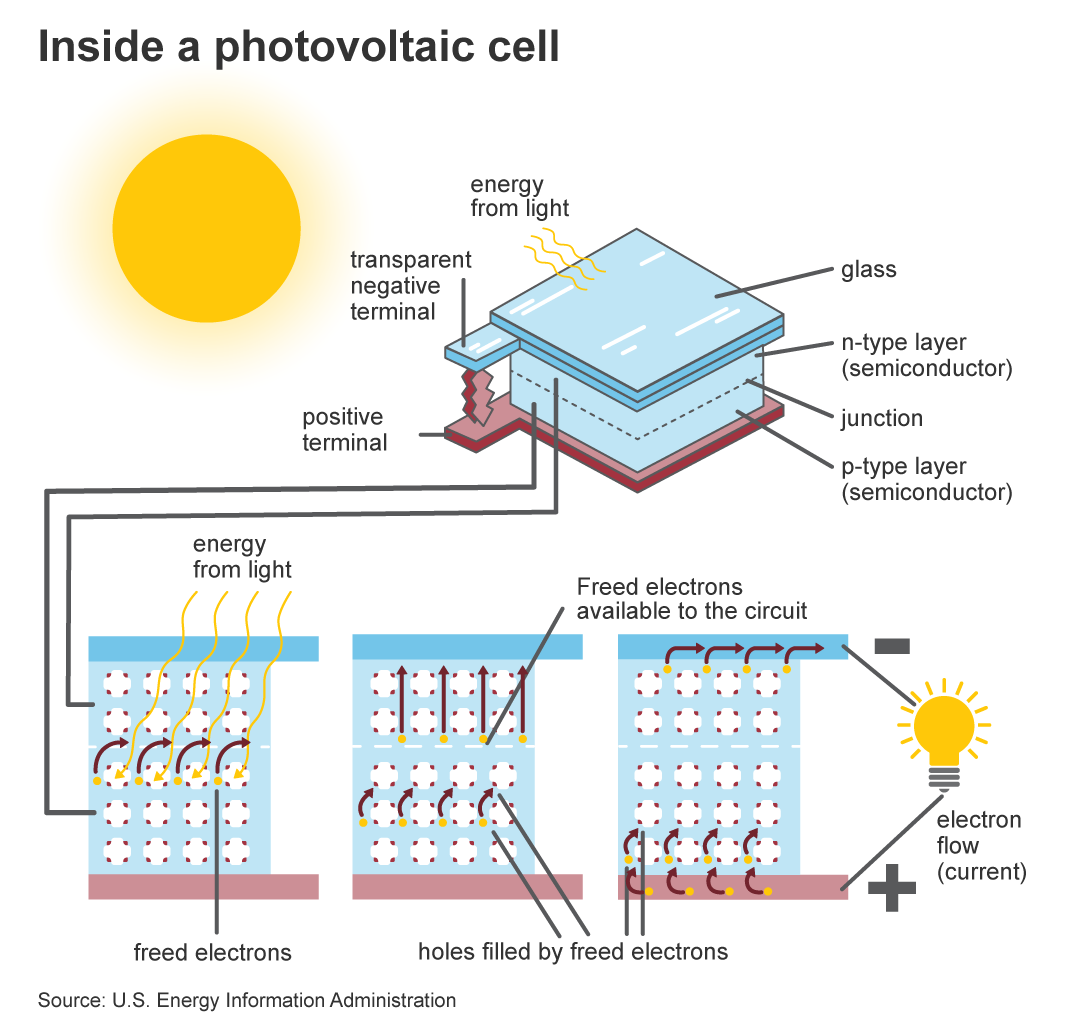
Photovoltaic systems are devices or setups that use solar cells to capture sunlight and convert it into usable electricity. Unlike traditional power generation methods (like burning fossil fuels), photovoltaic systems don’t rely on any moving parts or combustion processes. Instead, they use a natural phenomenon called the photovoltaic effect, discovered back in 1839 by French physicist Alexandre Edmond Becquerel.
Here’s how it works in a nutshell:
- Light hits the solar panel. Sunlight contains particles called photons, which carry energy.
- Solar cells absorb the photons. These cells, typically made of silicon, have special properties that allow them to release electrons when exposed to sunlight.
- Electricity is created. The released electrons flow through the material, creating an electric current that can be captured and used to power your home, business, or even your electric car.
How Photovoltaic Systems Work
Let’s take a closer look at the science behind the magic:
- Solar Panels (Modules): The visible part of the system that absorbs sunlight. Each panel is made up of smaller units called solar cells.
- Inverters: These devices convert the direct current (DC) electricity generated by the solar panels into alternating current (AC), which is the type of electricity used in most homes and businesses.
- Battery Storage (Optional): Some systems include batteries to store excess electricity for use when the sun isn’t shining.
- Electric Grid Connection: Many photovoltaic systems are tied to the local grid, allowing homeowners to sell unused electricity back to their utility company (a process known as net metering).
Common Uses of Photovoltaic Technology
The versatility of photovoltaic systems is one of their greatest strengths. Here are a few ways they’re used:
- Residential Power Generation: Homeowners can install PV panels on their rooftops to lower their electricity bills and reduce their reliance on the grid.
- Commercial and Industrial Applications: Businesses use large PV systems to offset energy costs and meet sustainability goals. For example, Google powers many of its data centers with solar energy.
- Solar Farms: These large-scale installations generate electricity for entire communities or regions. The Noor Solar Complex in Morocco, for instance, is one of the largest solar farms in the world.
- Portable Solar Gadgets: From solar-powered phone chargers to camping gear, portable PV technology is becoming more accessible and practical for everyday use.
The Growing Popularity of Photovoltaics
The adoption of photovoltaic technology has skyrocketed in recent years, and it’s no surprise why. The efficiency of solar cells has improved significantly, with modern panels converting up to 22% of sunlight into electricity—compared to just 6% a few decades ago. Combined with government incentives, falling installation costs, and increasing awareness of climate change, photovoltaic systems are becoming a go-to solution for renewable energy.
Case in point: Tesla’s Solar Roof is a prime example of how PV systems are blending seamlessly into everyday life, providing homeowners with sleek, efficient, and environmentally friendly energy options.
To sum up, photovoltaic systems are a revolutionary form of solar technology that turns sunlight into electricity with remarkable efficiency. They’re at the heart of the renewable energy movement, offering a clean, scalable, and increasingly affordable way to power the world.

Differences Between Photovoltaic and Solar
Now that we’ve covered what solar energy and photovoltaic systems are, let’s tackle the million-dollar question: Is photovoltaic the same as solar? By now, you’ve probably guessed the answer—no, they’re not the same. While photovoltaic technology is a type of solar energy system, there are other solar technologies that work differently and serve different purposes. Let’s explore the distinctions in greater depth.
Conceptual Differences
To keep it simple:
- Solar is the umbrella term for all technologies and methods that harness energy from the sun.
- Photovoltaic (PV) is a specific subset of solar energy that directly converts sunlight into electricity using solar panels.
Think of it this way: if solar energy were pizza, photovoltaic systems would be one specific topping—say, pepperoni. But there are other “toppings” too, like solar thermal and concentrated solar power, which we’ll discuss below.
Technical Distinctions
The main difference between photovoltaic systems and other types of solar technologies lies in how they use the sun’s energy.
- Photovoltaic Systems:
- Function: Convert sunlight directly into electricity.
- Technology: Use solar cells, usually made of silicon, to generate electricity through the photovoltaic effect.
- Applications: Powering homes, businesses, and gadgets; large-scale solar farms.
- Solar Thermal Systems:
- Function: Capture the sun’s heat instead of its light.
- Technology: Use panels or mirrors to absorb and transfer heat to water, air, or other fluids.
- Applications: Heating water for homes, swimming pools, or industrial processes. For example, solar water heaters are a common use of this technology.
- Concentrated Solar Power (CSP):
- Function: Uses mirrors or lenses to concentrate sunlight into a small area, generating high temperatures.
- Technology: This heat drives turbines to produce electricity, similar to a conventional power plant.
- Applications: Large-scale electricity generation, often for utility companies.
| Feature | Photovoltaic (PV) | Solar Thermal | Concentrated Solar Power (CSP) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Energy Source | Light | Heat | Heat |
| Output | Electricity | Hot water or air | Electricity |
| Technology | Solar panels (solar cells) | Solar collectors or tubes | Mirrors/lenses and turbines |
| Typical Use | Powering devices/buildings | Water/space heating | Large-scale electricity generation |
| Scale | Small to large (residential or industrial) | Small to medium | Large-scale utility projects |
Practical Applications of Each
So, when should you go with photovoltaic systems, and when is another type of solar technology the better choice?
- When to Choose Photovoltaic Systems:
- Ideal for generating electricity for homes, businesses, or communities.
- Great for off-grid locations where access to traditional electricity is limited.
- Useful in portable setups, like RVs or solar-powered gadgets.
- When to Use Solar Thermal Systems:
- Best for heating applications, such as warming your home or providing hot water.
- Suitable for swimming pools or industrial processes requiring heat.
- When to Opt for Concentrated Solar Power:
- A good choice for utility-scale electricity generation, especially in areas with lots of open space and abundant sunshine (e.g., deserts).
Why the Distinction Matters
Understanding the difference between photovoltaic systems and other types of solar technologies can save you money and frustration. For example:
- If you want to lower your electricity bill, PV panels are the way to go.
- If your primary goal is to reduce water-heating costs, a solar thermal system is more cost-effective.
By knowing which type of solar technology fits your needs, you can make smarter energy decisions and maximize your return on investment.
In short, while photovoltaic and solar are closely related, they are not interchangeable terms. Photovoltaic systems specialize in generating electricity, whereas other solar technologies may focus on heat production or large-scale power generation. This distinction is what makes solar energy so versatile—it can solve a variety of energy problems with different technologies tailored to specific needs.