Solar energy has become one of the hottest topics (pun intended) in the world of renewable energy, and for a good reason. With increasing electricity costs and a global push towards sustainable living, many people are asking the big question: Are photovoltaic panels better than solar panels?
If you’re scratching your head wondering whether there’s even a difference between the two, don’t worry—you’re not alone.

Let’s start with a quick clarification: all photovoltaic panels are solar panels, but not all solar panels are photovoltaic panels. Think of it like this—photovoltaic panels are a specific type of solar panel that focuses solely on generating electricity. In contrast, the term “solar panels” includes all technologies that harness the sun’s energy, including those that produce heat instead of electricity. It’s like comparing “cats” to “animals.” All cats are animals, but animals can also include dogs, elephants, or even dolphins (okay, maybe not in your backyard).
So, what exactly are photovoltaic panels? These panels use photovoltaic cells, typically made from silicon, to convert sunlight into electricity through a process called the photovoltaic effect. They’re the workhorses you see on rooftops and in solar farms, silently generating clean energy day after day.
On the other hand, solar panels is a broader term that encompasses:
- Photovoltaic panels (PV panels): Generate electricity.
- Solar thermal panels: Capture sunlight to heat water or air, making them ideal for residential heating systems or swimming pools.
- Hybrid systems: Combine PV and thermal technologies for dual-purpose use.
By understanding these distinctions, you’re already one step closer to figuring out whether photovoltaic panels might be the better choice for your needs.
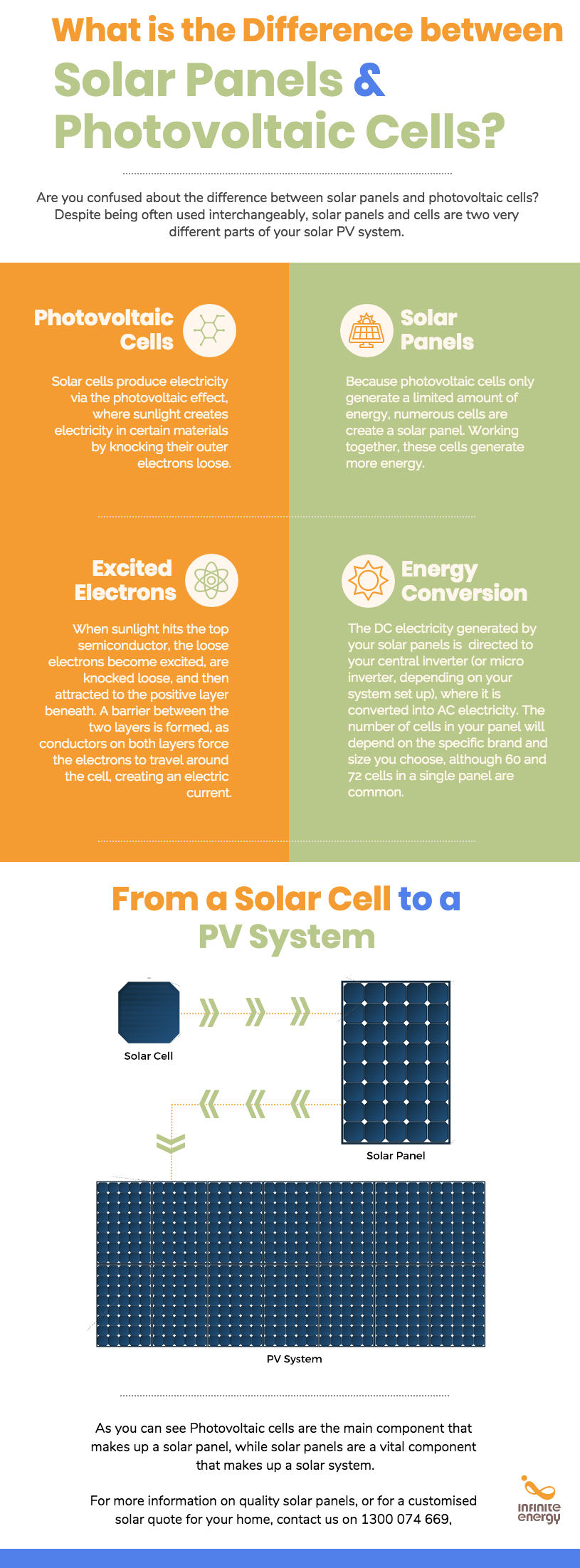
Differences Between Photovoltaic and Solar Panels
Let’s dive a little deeper. While both types of panels rely on sunshine, they’re designed for very different purposes:
- Photovoltaic Panels: Designed for electricity generation. They’re what power your lights, appliances, and—if you’re fancy—your electric car.
- Solar Thermal Panels: Specialized for heating, such as providing hot water for your home or business.
Here’s a handy comparison table to break it down:
| Feature | Photovoltaic Panels | Solar Thermal Panels |
|---|---|---|
| Function | Generate electricity | Produce heat |
| Primary Application | Powering homes, appliances, and EVs | Water heating, space heating |
| Technology | Uses photovoltaic cells | Uses sunlight to heat fluids |
| Efficiency in Task | High for electricity generation | High for heating applications |
| Storage Options | Can pair with batteries | Often uses insulated tanks |
Understanding these differences can help you avoid a common mistake: buying a solar thermal system when you actually needed a photovoltaic one (or vice versa). Trust me, it’s like ordering a salad when you really wanted pizza—disappointing.
Types of Solar Panels
Let’s zoom in on the technology within photovoltaic panels. There are several types, each with its pros and cons:
- Monocrystalline Panels: These are the premium choice, with high efficiency (up to 22%) and sleek aesthetics. They’re perfect for maximizing power in smaller spaces but tend to cost more.
- Polycrystalline Panels: A budget-friendly option, these are slightly less efficient (around 16–18%) but still a solid choice for homes with ample roof space.
- Thin-Film Panels: Flexible, lightweight, and great for unique installations, but they’re less efficient and take up more space to generate the same amount of energy.
Each of these types falls under the photovoltaic category, and your choice will depend on factors like your budget, available space, and energy needs.

Pros and Cons of Photovoltaic Panels and Solar Panels
Now that we’ve laid the groundwork, let’s get into the nitty-gritty: what are the advantages and disadvantages of photovoltaic panels and solar panels? This is where things start to get interesting—and a little practical.
Advantages of Photovoltaic Panels
Photovoltaic panels have been stealing the spotlight in the solar energy world, and for good reasons. Here’s why they’re so popular:
- High Efficiency for Electricity Generation
Photovoltaic panels are designed to convert sunlight directly into electricity, making them a fantastic option for households, businesses, and even large-scale solar farms. Monocrystalline PV panels, in particular, can achieve efficiency rates as high as 22%, giving you the most bang for your buck. - Scalability
Whether you want to power a single cabin in the woods or an entire neighborhood, photovoltaic systems are incredibly versatile. They can be scaled up or down depending on your energy needs and budget. - Compatibility with Battery Storage Systems
PV panels pair well with battery systems like the Tesla Powerwall, allowing you to store excess energy for use at night or during cloudy days. This is a game-changer for people in off-grid locations or areas prone to power outages. - Environmentally Friendly
Generating electricity without burning fossil fuels? That’s a huge win for the planet. By switching to PV panels, you’re significantly reducing your carbon footprint.
Disadvantages of Photovoltaic Panels
But hey, nothing’s perfect. Photovoltaic panels come with their own set of challenges:
- Higher Upfront Costs
Installing a PV system can set you back thousands of dollars. While costs have dropped significantly in the last decade, the initial investment can still be a hurdle for many households. - Dependence on Sunlight
PV panels work best under direct sunlight. Cloudy weather, shade from trees, or even dust on the panels can reduce their efficiency. If you live in Seattle, you might need backup solutions. - Complexity of Maintenance
While PV panels are generally low-maintenance, they do require occasional cleaning and inspection. And let’s not forget about the inverter and battery system, which need periodic checks.
Advantages of Solar Thermal Panels
Don’t count out solar thermal panels just yet! These systems are an excellent option for specific applications, particularly when heating is your primary concern.
- Cost-Effective for Heating Applications
Solar thermal panels are highly efficient at converting sunlight into heat. If your goal is to reduce heating bills, these systems are often more cost-effective than relying on traditional electricity-powered water heaters. - Simple Technology
Unlike photovoltaic panels, solar thermal systems have fewer moving parts. This simplicity makes them easier to install and maintain. - Ideal for High Heating Demands
Whether you’re heating a pool, a home, or even an industrial space, solar thermal panels excel in scenarios where large amounts of heat are needed.
Disadvantages of Solar Thermal Panels
As with any technology, there are some downsides to consider:
- Limited Functionality
Solar thermal panels are designed exclusively for heating purposes. If you’re looking to power your gadgets or appliances, they’re not going to cut it. - Space Requirements
Large solar thermal systems often require significant roof or ground space. For smaller homes or urban setups, this can be a dealbreaker. - Less Versatile Than PV Panels
Since they don’t generate electricity, solar thermal panels can’t run lights, electronics, or other appliances, making them less adaptable to varied energy needs.
Quick Recap of Pros and Cons
To help you digest all that information, here’s a side-by-side comparison of the pros and cons:
| Feature | Photovoltaic Panels | Solar Thermal Panels |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Benefit | Generates electricity for versatile use | Excellent for heating water or air |
| Initial Cost | Higher | Lower |
| Maintenance | Occasional cleaning and inspections required | Minimal, simpler system |
| Efficiency in Low Light | Decreases significantly | Less affected, but heating may slow down |
| Application | Powering homes, devices, and appliances | Heating applications only |
The debate about whether photovoltaic panels are better than solar panels really boils down to your individual energy needs. If you’re focused on electricity generation, PV panels are the clear winner. But if you need a reliable system for heating, solar thermal panels shine bright (literally).
Efficiency Comparison: Photovoltaic vs. Solar Thermal Panels
When it comes to solar technology, one of the most critical factors to evaluate is efficiency. After all, nobody wants to invest in a system that doesn’t give them the maximum return for their money—or their sunshine. Let’s break down how photovoltaic panels and solar thermal panels compare in this department and explore the real-world factors that influence their performance.
How Efficiency Is Measured
Efficiency in solar panels boils down to how effectively the system can convert sunlight into usable energy:
- For Photovoltaic Panels (PV): Efficiency is measured by the percentage of sunlight converted into electricity. For example, a 20% efficiency rating means that 20% of the sunlight hitting the panel is turned into electricity.
- For Solar Thermal Panels: Efficiency is measured by how well the system captures sunlight and converts it into heat. These panels typically have a much higher raw efficiency for heating tasks, often reaching 70–90%, as converting sunlight into heat is inherently less complex than generating electricity.
Photovoltaic Panel Efficiency
Photovoltaic panels are technological marvels, but their efficiency depends on several factors:
- Type of PV Panel:
- Monocrystalline Panels: High-end, with efficiency rates of 20–22%. Perfect for small spaces or premium installations.
- Polycrystalline Panels: Slightly less efficient, typically around 16–18%, but more affordable.
- Thin-Film Panels: Efficiency hovers between 10–12%, but they’re lightweight and flexible for unique applications.
- External Factors:
- Temperature: Believe it or not, extreme heat can reduce PV panel performance. A drop in efficiency of 0.3–0.5% per degree Celsius is typical. So while panels love the sun, they don’t enjoy baking under intense heat.
- Sunlight Intensity: More sunlight equals better performance, which is why geographic location matters.
- Orientation and Tilt: Panels must face the sun directly for optimal output. A south-facing roof in the Northern Hemisphere is ideal.
While the efficiency numbers for PV panels may seem modest compared to solar thermal, their versatility makes up for it. Generating electricity allows them to power virtually everything in your home, from your laptop to your refrigerator.
Solar Thermal Panel Efficiency
Solar thermal panels are rockstars in their own domain, especially when heating is the goal. Their high efficiency stems from their simplicity:
- Higher Energy Conversion Rates: Solar thermal systems typically convert 70–90% of the sunlight they receive into heat energy.
- Fewer External Influences: While PV panels falter on cloudy days, solar thermal systems can still generate heat effectively due to their reliance on insulated fluids or materials to retain warmth.
- Seasonal Considerations: Solar thermal panels perform exceptionally well in cold, sunny environments since they don’t need direct sunlight as intensely as PV panels.
That said, the key limitation of solar thermal panels is their single-purpose design. Unlike photovoltaic panels, which can multitask, solar thermal systems are exclusive to heating applications.
Real-World Efficiency Comparisons
To bring the comparison to life, here’s a practical look at how these systems perform in real-world conditions:
| Scenario | Photovoltaic Panels | Solar Thermal Panels |
|---|---|---|
| Efficiency in Sunny Climates | High, especially for monocrystalline panels | Extremely high, ideal for heating systems |
| Efficiency in Cloudy Climates | Reduced output but functional with battery backup | Still effective for heating purposes |
| Energy Storage | Requires batteries (e.g., lithium-ion systems) | Relies on insulated tanks for heat retention |
| Space Efficiency | High, especially with monocrystalline panels | Requires larger setups for high heating needs |
For example, if you live in sunny California and your main concern is slashing your electricity bill, photovoltaic panels are the clear winner. However, if you’re in a colder region like Minnesota and want a consistent supply of hot water, solar thermal panels might be the better fit.
Which Is More Efficient for Specific Needs?
It all boils down to your goals:
- If you need electricity for your home, appliances, or electric car, photovoltaic panels are unmatched in their versatility.
- If you need hot water or heating for your home or pool, solar thermal panels are far more efficient and cost-effective for this specific task.
Efficiency is an important metric, but remember: it’s not just about numbers. It’s about how well a system meets your unique energy needs. A highly efficient system in one area may not be practical or cost-effective for another, so always consider the full picture before deciding.
Cost Analysis of Photovoltaic Panels vs. Solar Panels
When deciding between photovoltaic panels and solar thermal panels, understanding the costs involved is crucial. After all, solar energy is an investment, and you’ll want to ensure you’re making a choice that aligns with both your budget and your energy goals.
Initial Costs
The upfront cost of installing a solar energy system depends on the type of panel, installation requirements, and system size. Here’s how the numbers stack up:
Photovoltaic Panels (PV Panels):
- Average Cost per Watt: Around $2.50–$3.50 in the U.S. (2025 estimates).
- System Size: Most residential PV systems are between 5–10 kW, meaning the total cost typically ranges from $12,500 to $35,000 (before tax credits).
- Incentives: Federal tax credits, local rebates, and net metering programs can significantly reduce these costs. For instance, the federal solar investment tax credit (ITC) currently offers a 30% deduction, lowering the cost of a $20,000 system to $14,000.
Solar Thermal Panels:
- System Costs: Generally cheaper upfront, with prices ranging between $3,000 and $7,000 for a residential system.
- Simplicity of Installation: Solar thermal systems often have fewer components, which can further reduce labor costs.
It’s worth noting that while solar thermal panels are initially cheaper, their limited functionality (heating only) may require you to invest in additional systems for electricity needs.
Long-Term Savings
Here’s where solar really starts to pay off:
- Photovoltaic Panels:
- A typical PV system can reduce your electricity bill by 50–90%, depending on your energy usage and local utility rates.
- Over 25 years (the average lifespan of most PV panels), savings can range from $10,000 to $30,000 or more.
- If paired with a battery, you can further maximize savings by storing excess energy and avoiding peak utility rates.
- Solar Thermal Panels:
- Solar thermal systems can slash heating bills by 50–80%, especially in regions with high heating demands.
- While the monetary savings may be less compared to PV panels (since heating typically accounts for a smaller portion of energy costs), the return on investment can still be significant for households with high hot water usage.
Maintenance Costs
Both systems are generally low-maintenance, but there are differences in upkeep requirements:
Photovoltaic Panels:
- Routine Maintenance: Requires occasional cleaning (especially in dusty or polluted areas) to maintain efficiency. Expect to pay $150–$300 per cleaning, depending on the system size.
- Component Replacement: The inverter (which converts DC electricity to AC) typically needs to be replaced after 10–15 years, costing around $1,000–$2,500. Batteries, if used, also have a lifespan of about 10 years.
Solar Thermal Panels:
- Maintenance Needs: Minimal. These systems have fewer components, so they require less upkeep. Inspections every few years to check for leaks, insulation issues, or pump malfunctions are sufficient.
- Durability: Solar thermal panels tend to last longer (30+ years) due to their simpler design.
Total Cost Comparison
To give you a clearer picture, here’s a summary of the total cost breakdown over 25 years for a typical residential setup:
| Category | Photovoltaic Panels (5kW System) | Solar Thermal Panels (for Heating) |
|---|---|---|
| Upfront Cost (Before Incentives) | $15,000–$20,000 | $3,000–$7,000 |
| Lifespan | 25–30 years | 30+ years |
| Maintenance Costs | $2,000–$5,000 | $500–$1,500 |
| Lifetime Savings | $20,000–$50,000+ | $5,000–$15,000 |
Which Option Offers Better Value?
- Go for Photovoltaic Panels if:
- Your electricity costs are high, and you want to maximize long-term savings.
- You’re looking for versatility, such as powering your home, appliances, and electric vehicle.
- Incentives in your area make the upfront investment more affordable.
- Choose Solar Thermal Panels if:
- Your primary goal is to reduce heating costs.
- You have a limited budget and don’t need electricity generation.
- You’re in a region with high heating demands and moderate sunlight.
While photovoltaic panels come with a heftier price tag, their versatility and ability to generate electricity make them a better overall investment for most households. That said, solar thermal panels shouldn’t be overlooked for niche applications like water heating or industrial use.